We assure you that you won’t be alone on your journey towards becoming your healthier self.
Health & Wellness
Can’t Figure Out Those White Blemishes On The Skin? Know The Causes, Treatments And Prevention Methods

Many individuals may worry about white spots on their skin, leading to decreased self-assurance and self-belief. Understanding the causes and how to deal with them is crucial, as these markings may range from tiny white dots to bigger areas.
White blemishes refer to areas of skin that appear lighter than the surrounding skin due to a loss or reduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. They can affect people of all ages and skin types. While they are usually harmless, their appearance can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions or skin disorders. This detailed blog examines the typical causes of white blemishes on the skin and treatment options.
Table Of Contents
1. What Causes White Blemishes On The Skin?
2. How Do I Get Rid Of White Patches On My Skin? Potential Treatment Options
3. What Deficiency Causes White Patches?
4. How To Clear Blemishes On Skin? Natural Prevention Methods
5. Dietitian's Recommendation
6. The Final Say
7. FAQs
8. References
What Causes White Blemishes On The Skin?
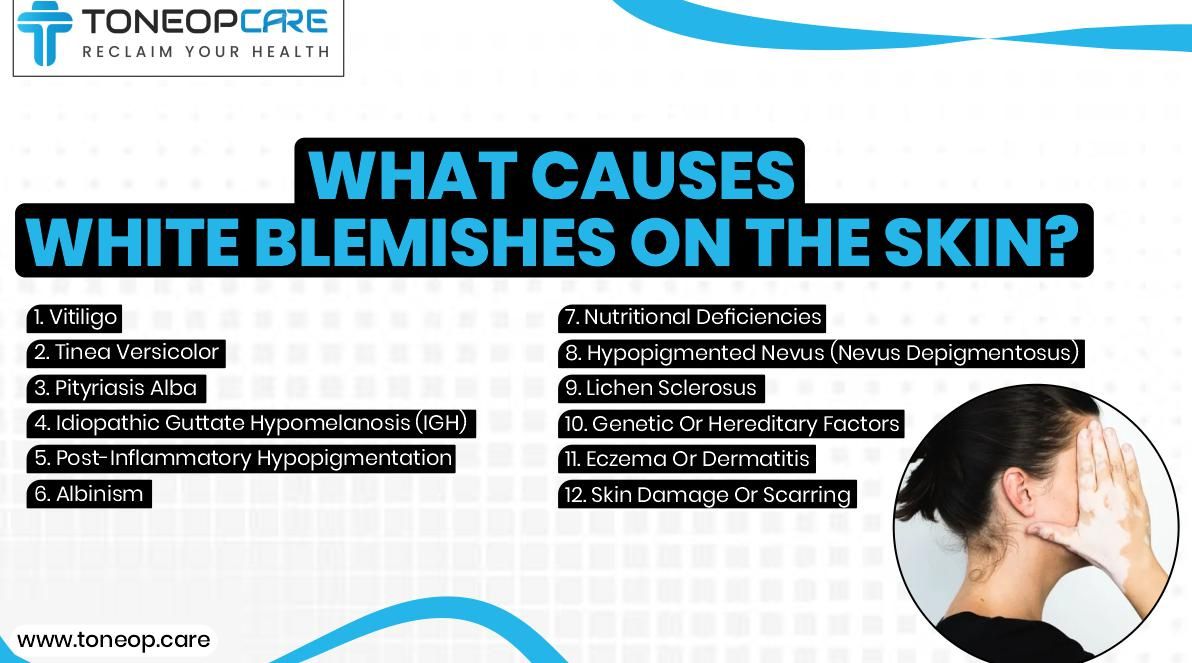
What is the reason for the white patches on the face? Here are 12 causes of white blemishes on the skin:
1. Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a condition in which the immune system targets melanocytes, the cells that create skin pigment called melanin. White patches that are not regular and may spread slowly over some time. It typically impacts regions such as the facial area, hands, upper limbs, and knees. Genetic factors, stress, or contact with specific substances trigger vitiligo.
2. Tinea Versicolor
This is a fungal infection caused by Malassezia yeast, which disrupts skin pigmentation. Small, white or discoloured patches that may itch or become more noticeable in warm and humid conditions. It typically affects the chest, back, shoulders, and neck. Oily skin, excessive sweating, and living in hot climates may trigger it.
3. Pityriasis Alba
This is a benign skin condition which is often seen in children and teenagers. It is linked to dry skin and mild inflammation. It appears as scaly, pale patches, usually on the face, neck, or arms and is more evident in people with deeper skin tones. People with a history of eczema or atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop this condition.
4. Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis (IGH)
A common condition in older adults characterised by small white spots on sun-exposed areas. Flat, round white spots, typically on the arms, legs, or face, appear on people suffering from IGH. It is often associated with cumulative sun exposure and ageing. Fair skin and prolonged UV exposure may worsen the situation for a person with IGH.
5. Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
Occurs when the skin loses pigment after inflammation or trauma, such as burns, infections, or chronic conditions like psoriasis. White patches in areas previously affected by inflammation may appear. Frequently temporary but post-inflammatory hypopigmentation may endure in certain instances. Chronic inflammatory conditions and delayed wound healing may trigger it.
Also Read: 10 Anti-Inflammatory Foods For Skin, Diet Plan For Psoriasis & Ways To Reduce It
6. Albinism
Albinism is an uncommon genetic disorder resulting from insufficient melanin production in the skin, hair, and eyes. Uniformly pale skin, light hair, and eye colour may start appearing with albinism. You may develop elevated sensitivity to the sun and greater susceptibility to skin cancer. Inherited mutations in genes related to melanin production may make some people more susceptible to albinism.
7. Nutritional Deficiencies
Insufficient intake of essential nutrients can significantly impact skin health and pigmentation. Light spots or patches on the skin, often accompanied by symptoms like fatigue or brittle nails, may indicate nutritional deficiencies such as vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D3 deficiency, calcium, vitamin B12, copper, or biotin deficiency.
These deficiencies can arise from poor diet, malabsorption syndromes, or chronic illnesses. It's important to address these issues to maintain healthy skin and overall well-being.
8. Hypopigmented Nevus (Nevus Depigmentosus)
A congenital condition where specific areas of the skin lack pigmentation. Well-defined, stable white patches are present from birth in this condition. It does not spread or change significantly over time. The risk factor involves genetic factors.
9. Lichen Sclerosus
A chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause depigmentation and scarring. White, shiny patches are often found on genital or anal areas, but they can appear elsewhere. It may cause discomfort or itching. Hormonal imbalances and autoimmune tendencies may trigger lichen sclerosus.
10. Genetic Or Hereditary Factors
Some skin conditions causing white blemishes, such as vitiligo or albinism, are inherited. If a person has a family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases, they may be more likely to develop white patches. Similarly, some individuals may inherit a predisposition to fungal infections like tinea versicolor, which can cause lighter skin patches.
11. Eczema Or Dermatitis
Chronic skin inflammation like eczema can lead to hypopigmented spots as the skin heals. Patches of dry, flaky skin that may turn lighter as they recover. Allergies, irritants, or a history of atopic dermatitis may make you prone to it.
12. Skin Damage Or Scarring
Injuries, burns, or surgical scars can result in lighter skin in the affected area due to loss of melanin production. White patches or streaks in areas with previous trauma may result in skin damage or scars.
ToneOp Care’s Skin 360 Tablets are an age-defying 360 skincare for glowing skin, reduced pigmentation, treating acne and skin disorders and promoting even skin tone.
Also Read: Which Deficiency Causes Dry Skin? Know 6 Vitamins And Minerals To Consider!
How Do I Get Rid Of White Patches On My Skin? Potential Treatment Options
Getting rid of white patches on your skin depends on their cause, so it’s essential to first identify the underlying condition. White patches are often harmless, but they can be treated or improved with medical and home remedies like:
- Fungal Infections: For fungal infections like tinea versicolor, antifungal creams, lotions, or oral medications prescribed by a doctor can help clear the infection and restore normal pigmentation.
Also Read: Fungal Infection In the Stomach: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment Methods
- Vitiligo: If the patches are due to vitiligo, treatment focuses on restoring skin colour. Options include topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or light therapy such as PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) or narrowband UVB therapy. For stubborn cases, procedures like skin grafting or melanocyte transplantation might be considered.
- Pityriasis Alba: In cases of pityriasis alba or post-inflammatory hypopigmentation, moisturising creams and mild topical steroids can improve the skin’s appearance. These often resolve naturally over time.
- Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis: For white spots caused by idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (small white sunspots), protection from UV rays and gentle exfoliation may help.
Home remedies like aloe vera, coconut oil, or antifungal solutions (like diluted apple cider vinegar) may soothe the skin or aid fungal treatment.
What Deficiency Causes White Patches?
White patches on the skin can sometimes result from nutritional deficiencies, which affect melanin production or skin health. The most common deficiencies associated with white patches are:
1. Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells and the preservation of nerve health. A lack of melanin production can result in decreased pigmentation, resulting in white or pale patches. This is frequently observed in people with pernicious anemia or inadequate dietary intake.
2. Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D is involved in the renewal of skin cells and in the functioning of the immune system. Low levels may contribute to conditions like vitiligo, which causes white patches.
Insufficient vitamin D may disrupt the normal function of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in vitiligo, where the skin loses pigment and develops white patches. In tinea versicolor, a fungal infection that causes lighter patches and low vitamin D levels, it can weaken the immune system, making it easier for the infection to spread.
3. Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is vital for healthy skin. Its deficiency may disrupt skin cell function, leading to white spots or patches. A calcium deficiency can hamper these cells' ability to operate, resulting in white spots on the skin. A calcium shortage can also impair immunity and increase susceptibility to tinea versicolor, a fungal illness resulting in white skin spots.
Also Read: 11 Warning Signs of Calcium Deficiency: Tooth Decay, Fractures, Fatigue and More
4. Copper Deficiency
Copper is crucial for melanin synthesis. A lack of this mineral can interfere with pigmentation and result in white spots. These patches are more commonly seen in areas like the face, hands, and other sun-exposed areas.
Additionally, copper is involved in the health of blood vessels and connective tissues, and a deficiency can also contribute to skin discolouration, as well as other symptoms like fatigue and weakened immune function.
How To Clear Blemishes On Skin? Natural Prevention Methods
White blemishes on the skin, often caused by conditions like vitiligo, tinea versicolor, or even fungal infections, can be distressing and affect one’s appearance. Preventing these blemishes involves:
- Protect Skin From Sun Damage: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, wear protective clothing and hats and avoid excessive sun exposure during peak hours.
- Maintain Skin Hygiene: Cleanse the skin on a regular basis to avoid fungal infections and use gentle, non-irritating skin products for cleansing.
- Stay Hydrated And Nourished: Make sure to consume a sufficient amount of water to keep your skin hydrated and eat a well-rounded diet full of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Manage Chronic Skin Conditions: Follow treatment plans for eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis and avoid scratching or picking at affected areas which maybe the most difficult to resist.
Dietitian's Recommendation
To compensate for the lack of nutrients, eat foods that are high in these essential elements, like fish, eggs, dairy, leafy greens, nuts, and fortified cereals. Sometimes, supplements might be necessary, but it's crucial to consult a professional to verify the deficiency before beginning any treatment.
Dt. Akshata Gandevikar
The Final Say
If you see white blemishes on the skin, it's important to understand what might be causing them. These blemishes can come from nutritional deficiencies, sun exposure, or skin conditions. You can treat them with creams or by eating healthy foods. To prevent these blemishes, make sure to protect your skin from the sun and eat a balanced diet full of vitamins. If you're ever unsure, it's always a good idea to talk to a doctor for help!
FAQs
1. Do white blemishes go away on their own?
Some white blemishes, like those from pityriasis alba or post-inflammatory hypopigmentation, often resolve naturally over time. Others, like vitiligo or idiopathic guttate hypomelanotic, may persist and require treatment for improvement.
2. Are white blemishes harmful?
Most white blemishes are harmless, such as those from conditions like pityriasis alba or idiopathic guttate hypomelanotic. However, some, like vitiligo or fungal infections, may need medical attention for diagnosis and management.
3. Can white blemishes be treated?
Yes, treatment depends on the cause. Options include antifungal creams, corticosteroids, light therapy, and skin grafting for severe cases. Moisturisers and sunscreen help improve and protect affected areas.
4. How is vitiligo different from other white blemishes?
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition causing progressive, symmetrical white patches due to melanocyte loss. Unlike fungal infections or hypopigmentation, vitiligo is often permanent and may require treatments like light therapy or grafting.
References
- https://www.carehospitals.com/blog-detail/white-patches-on-skin/
- https://www.tuasaude.com/en/white-spots-on-skin/
- https://www.sknclinics.co.uk/conditions/white-spots
- https://www.truemeds.in/blog/white-spots-on-skin
- https://www.bodycraft.co.in/blogs/white-spots-on-skin/
About ToneOp Care
ToneOp Care is the ultimate destination for high-quality nutraceutical supplements and ayurvedic products in India! We are proud to offer a significant range of products designed to support your health and well-being, including weight loss, muscle gain, immunity, skin and hair care, and women's health. All our products are manufactured in India using the latest technology and facilities, ensuring the highest quality standards.


